What Is Net Profit Margin? Definition, Formula, And Examples
Profitability, sometimes called profit margin or net margin, is determined by calculating income as a percentage of revenue. The two figures that we need for this calculation are found in the income professional invoice design statement. Net income margin is the net after-tax income of a business, expressed as a percentage of sales. It is used in ratio analysis to determine the proportional profitability of a business.
Formula for Calculating Net Income Component Percentage
- If you look at an income statement template, you can find it at the bottom as the value in the bottom line.
- It is the ratio of net profits to revenues for a company or business segment.
- Then, subtract any depreciation and SG&A (selling, general, and administrative) expenses from gross profit to find the operating margin — also referred to as earnings before interest and taxes or EBIT.
- The definition of a good net profit margin depends on several factors, including industry standards, business models, and the company’s specific circumstances.
To calculate your profit margin, you have to calculate your net income and net sales first and then utilize the profit margin formula once you have identified your net income and net sales. A high percentage means that the company did well in managing its expenses. It is also useful to compare it to a benchmark, such as industry average or past performance, to determine the company’s standing. Net profit margin, or simply net margin, measures how much net income or profit a company generates as a percentage of its revenue. It is the ratio of net profits to revenues for a company or business segment. For the purpose of this ratio, net profit is the net income or net profit of the entity as exhibited by its income statement or profit and loss account.
Company
As a result, the company has greater depreciation expenses, reducing net income despite the impressive cash flow. Data from the NYU Stern School of Business shows that the average net profit margin for the shoe industry is 12.57%, which means that Nike is in line with the market (1). However, this number alone is not enough to judge the value of a business — it should be one factor in a larger analysis.
How to calculate the net profit margin
Put another way, a net profit margin of 12% means that for every dollar generated by Nike in sales, the company kept $0.12 as profit. This measurement provides an overall picture of a company’s profitability, and investors can use it to see how well a company is generating a profit compared to costs. The ratio of net income to sales essentially expresses the overall cost and price effectiveness of the business. This ratio provides an indication of the buffer available in case of higher costs or lower sales in the future.
MANAGING YOUR MONEY
It is also worth noting that depreciation and amortization may also be deducted from revenues when calculating net income. Investors can assess if a company’s management is generating enough profit from its sales and whether operating costs and overhead costs are being contained. In a nutshell, net income is the amount of money your business generates after paying all expenses. And, expressing this as a percentage can be a good way to assess profitability. The result of these calculations is displayed in percentages, but you may also express them in decimal form (e.g., 13% becomes 0.13). Note that the net profit margin ratio is not the same as [profit margin of the business you’re trying to analyze.
What Is the Implication of Net Income Component Percentage?
The net profit margin works to show how well your business converts its sales into profits. In other words, the percentage was estimated by the net profit margin equation, which is the percentage of your revenues that are the revenues your company gets to keep. On the contrary, this ratio also shows the amount of revenue you are about to skip through fees and costs that go along with your business. It can help find out whether a business should concentrate on whittling back spending. You can see that both the net sales and net income are referred to each other, in that expenses can expand the prices and reduce the sales (based on your goods and audience).
Once you’ve calculated the net income (profit), simply divide this amount by the total revenue. Sales is the income a company generates by selling its goods and services. Meanwhile, revenue is a business’s income from all sources, including sales. For example, a company can have $10 million in sales but $12 million in revenue if nonoperating income totals $2 million. Net sales revenue is gross sales revenue minus any returns, discounts, or allowances. Net sales is a more accurate representation of the cash a company brings in from customers.
A deeper analysis of the figures above would reveal that the company incurred significantly high cost of sales and operating expenses in Year 2. However, the net profit margin is not merely the amount of cash left in the company after all costs (e.g., salaries, utilities, or depreciation) are covered. In order to get your hands on the net profit, you have to consider all of the operating expenses, interest expenses, and taxes.
Note how easy it is to merge this information into one comparable indicator. Common size financial statements help to analyze and compare a company’s performance over several periods with varying sales figures. The common size percentages can be subsequently compared to those of competitors to determine how the company is performing relative to the industry.
However, the gross profit margin is also important to investors because an increase over time means a company is becoming more efficient and bringing in more revenue per product sold. Similarly, patent-secured businesses like pharmaceutical companies may incur high research costs initially, but reap high profit margins when they bring a new drug to market. Business owners, company management, and external consultants use it internally for addressing operational issues and to study seasonal patterns and corporate performance during different time frames. A zero or negative profit margin translates to a business that’s either struggling to manage its expenses or failing to achieve good sales. Drilling it down further helps to identify the leaking areas—like high unsold inventory, excess or underutilized employees and resources, or high rentals—and then to devise appropriate action plans.
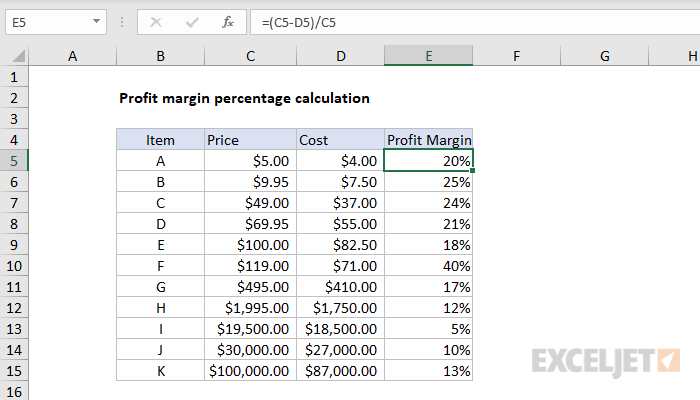
A net profit margin of 20% means that for every dollar of revenue generated, the company retains 20 cents as net profit. This indicates that the company has effective cost management and is able to generate a reasonable level of profitability from its operations. A 20% net profit margin is generally considered good, but its significance may vary across industries. Profit margin is a common measure of the degree to which a company or a particular business activity makes money.
